What is Retaining Wall ?
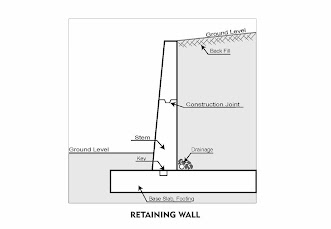
Retaining wall are relatively rigid walls used for supporting soil laterally so that it can be retained at different levels on the two sides. Retaining walls are structures designed to restrain soil to a slope that it would not naturally keep to (typically a steep, near-vertical or vertical slope).
They are used to bound soils between two different elevations often in areas of terrain possessing undesirable slopes or in areas where the landscape needs to be shaped severely and engineered for more specific purposes like hillside farming or roadway overpasses. The most important consideration in proper design and installation of a retaining wall is to recognize and counteract the tendency of the retained material to move downslope due to gravity. It is important to have proper drainage behind the wall in order to limit the pressure to the wall design value. Drainage material will reduce or eliminate the hydrostatic pressure and improve the stability of the material behind the wall.
Types Of Retaining Wall
- Gravity Retaining Wall
- Reinforced Retaining Wall
- Concrete Cantilever Wall
- Buttressed Retaining Wall
- Reinforced Soil Retaining Wall
- Green Retaining Wall
- Mechanical Stabilization Wall
- Anchored Wall
1. Gravity Retaining Wall
Gravity wall depend on their mass to resist pressure from behind and may have better setback to improve stability by leaning back towards the retained soil. For short landscaping walls, they are often made from mortarless stone and segment concrete units. Dry stacked gravity walls is somewhat flexible and do not require a rigid footing.
2. Reinforced Retaining Wall
Reinforced concrete and reinforced masonry walls on spread foundation are gravity structures in which the stability against overturning is provided by the weight of the wall and reinforcement bars in the walls.
3. Concrete Cantilever Wall
A concrete cantilever retaining wall is one that consists of a wall that is connected to the foundation. A cantilevered wall holds back a significant amount of soil, so it must be well engineered. They are the most common type used as retaining walls. Cantilever wall rest on a slab foundation. This slab foundation is also loaded by back-fill and thus the weight of the back-fill and surcharge also stabilizes the wall against overturning and sliding.
4. Buttressed Retaining Wall
Buttressed retaining wall are cantilever wall straightened with counter forts monolithic with the back of the wall slab and base slab. The counter-forts act as tension stiffeners and connect the wall slab and the base to reduce the bending and shearing stresses. To reduce the bending moments in vertical walls of the great height, counterforts and used, spaced at distances from each other equal to or slightly larger than one-half of the height counter forts are used for high walls with heights greater than 8 to 12 m.
5. Reinforced Soil Retaining Wall
Reinforced soil can also be used as retaining walls if they are built as an integral part of the design and to act as an alternative to the use of reinforced concrete or other solutions on the grounds of economy or as a result of the ground conditions.
6. Green Retaining Wall
Green retaining walls can be used to retain more gentle slopes. A Geo cellular structure such as a series of honeycomb cells can be embedded into the surface of the slope to stabilize it, and the individual cells can then be planed.
7. Mechanical Stabilization Wall
Mechanically stabilized earth walls are walls that can tolerate some differential movement. The wall face is infilled with granular soil whilst retaining the backfill soil.
8. Anchored Wall
An anchored retaining wall can be constructed in any of the aforementioned styles but also includes additionals strength using cables or other stays anchored in the rock or soil behind. It usually driven into the material with boring, anchors and then expanded at the end of the cable, either by mechanical means or often by injecting pressurized concrete which expands to form a bulb in the soil.









No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, Please let me know.