Bearing Capacity of Soil
The bearing capacity of soil is the ability of soil to safely carry the pressure placed on the soil from any engineered structure without undergoing a shear failure with accompanying large settlements.Bearing capacity of soil is influenced by many factors which are load related or non-load related factors that is why during the design of structure bearing capacity of soil need to be considered.
Following are the factors influencing bearing capacity of soil:
- Soil Strength
- Width of foundation
- Depth of foundation
- Soil weight and surcharge
- Spacing Between Foundation
- Subsurface Voids
- Frost Action
- Soil Reinforcement
- Soil Erosion
- Earthquake
1. Soil Strength
Bearing capacity of cohesionless soil and mixed soil increases unproportionally with the increase of in the effective friction angle.However bearing capacity of cohesive soil varies linearly with the soil cohesion provided that the effective friction angle is zero.
2. Width of Foundation
Width of foundation affects bearing of cohesionless soil.The bearing capacity of a footing placed at the surface of cohesionless soil, where the soil shear strength is considerably dependent on internal friction, is proportional to the width of the foundation.
3. Depth of Foundation
Depth of foundation influence the bearing capacity of soil,This because if the bearing capacity is high depth of foundation is more.This is specifically obvious in a uniform cohesionless soil.
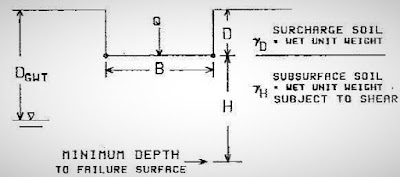
4. Soil Weight and Surcharge
The contribution of subsurface soil, which are influenced by water table to the bearing capacity cannot be ignored.The water table should not be above the base of the foundation to avoid construction, seepage and uplift problems.
5. Spacing Between Foundation
The minimum horizontal distance between the two foundations should be at least equal to the width of the wider one.The minimum spacing between the foundation should be 1.5 times foundation width, during the design of foundation in order to avoid reduction in bearing capacity.
6. Subsurface Voids
Bearing capacity of soil decreases due to subsurface voids which are within a critical depth beneath the foundation.The critical depth is that depth below which the influence of pressure in the soil from the foundation is negligible.
7. Frost Action
Frost heave in certain soils in contact with water and subject to freezing temperature or loss of strength of frozen soil upon thawing can alter bearing capacity over time.Low cohesion materials containing a high percentage of silt-sized particle are mostly susceptible to frost action.
8. Soil Reinforcement
Soil reinforcement is a technique used to improve the stiffness and strength of soil to resist more load.This method is adopted where the soil stata is weak and soil is susceptible.Bearing capacity of soft or weak soil can be increased greatly by installing various forms of reinforcement in the soil like metal ties, strips or grids geotextile fabrics or granular materials.
9. Soil Erosion
Erosion of soil around and under foundations are seepage can reduce bearing capacity and can cause foundation failure.
10. Earthquake
Repeated movements could increase pore pressure in foundation soil and consequently bearing capacity is decrease.Sources of cyclic movements are earthquakes, vibrating machinery, blasting and pile driving.The foundation soil can liquify when the effective stress of soil is reduced to essentially zero.This may be initiated by either monotonic loading or cyclic loading.










No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, Please let me know.